
Python实现单链表增删改查
Python实现单链表
自己在看书的时候忘记是哪个老师说的,数据归根到底其实就是2种,一种是链表,一种是数组。其他的什么栈堆队列集合都是从这两种数据类型转换过来的。那今天我就开始自己写写试试看吧。从今天开始重新苦逼的算法之路。第一路就是单链表的实现,什么是单链表呢。节点就是一个有头有身体的数据,这个头连接的就是自己的上一个链表的位置。
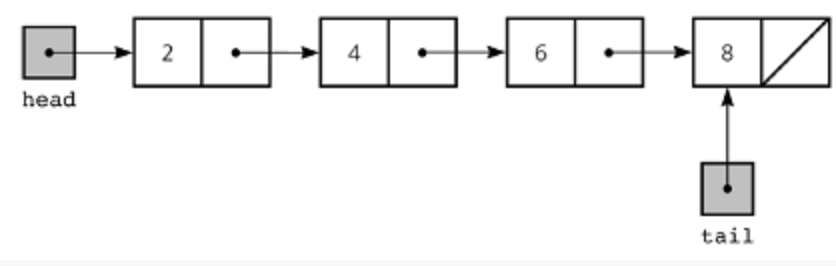
参考网页:https://www.tutorialspoint.com/python_ata_structure/python_linked_lists.htm
从上面的图可以看出来,其实链表除了头和尾都有一个分为两部分。链表也分为单链表,双链表,循环链表,非循环列表。
这一次就实现最简单的单链表。根据万能的增删改查定律,一个链表我们只要实现了增删改查遍历啥的差不多就能说是实现了。比如我们用的Python的什么集合和列表还有元祖,本质上不就是进行操作各种数据的增删改查吗?
""" 新建一个节点类 包含数据和尾巴(默认为空) """ class Node(object): def __init__(self, data): self.data = data # 数据位置 self.next = None # 表示信息 """ 新建一个单链表 单链表上有个头""" class SingleLinkedList(object): # 初始化生成链表的头,私有是因为不想轻易被改变 def __init__(self, node=None): self.__head = node """ 判断是否为空 head指向了默认的node 初始化的时候已经生成了一个__head,指向了空 所以判断是否为空的时候就要判断头是否为空 因为不为空的链表的头,应该是有数的,并且指向前面的屁股 """ def is_empty(self): return self.__head == None """ 链表长度 思路: 链表头复制给current->设置一个count用来计数->while判断 -> 只要current不为None 意思就是只要现在不是尾巴 没到头 -> 计数+1->然后current.next就要赋值给current -> 因为链表的特性:尾巴就是下一个链表的头 """ def length(self): current = self.__head count = 0 while current != None: count += 1 current = current.next return count """ 遍历 思路: 其实遍历的思路和上面的计算长度几乎差不多,都是头判断然后进行输出 赋值头部 -> 进行判断是否为最后一个-> 不是就进行打印 -> current.next就要赋值给current-> 因为链表的特性:尾巴就是下一个链表的头 """ def travel(self): current = self.__head while current != None: print(current.data) current = current.next """ 尾部添加 新建一个节点 判断链表是否为空 不为空,就现在新建的链表头指向前面链表的屁股 前面的链表是什么呢?如果没有这个疑问,很容易就会写错 前面的链表其实就是现在链表的最后一个 最后一个是什么呢,最后一个孤独的链表就是没有尾巴的链表 没有尾巴的链表就是next没有任何值的链表 """ def append(self, data): node = Node(data) if self.is_empty(): self.__head = node else: current = self.__head while current.next != None: current = current.next # 到这里都是一直向下走 # 这里基本表示走到了尽头 current.next = node """ 头部添加 """ def add(self,data): # 新建节点 node = Node(data) # 新建节点的尾巴指向现在链表的头 node.next = self.__head # 于是孤独节点的头就成了现在的头 self.__head = node """ 添加到指定位置 positon:头插(add) 尾插(append) 中间插入 位置是索引int data:节点数据 """ def insert(self, position, data): if position <= 0: self.add(data) # 直接使用上面定义的 elif position > (self.length()-1): self.append(data) else: node = Node(data) count = 0 # 记录插入位置的前一个位置 # [4,6,7,2,3] 假设输入position是2 # [4,6,X,7,2,3] 那是不是就要找到6的位置 pre就是这个位置 pre = self.__head while count < (position -1): count += 1 # 下一个列表的前面就是后面 pre = pre.next # self.__head.next node.next = pre.next pre.next = node """ 查找节点 判断是否为空,为空直接False 继续遍历向下走 """ def search(self, data): current = self.__head while current != None: if current.data == data: return True current = current.next return False """ 删除节点 删除要先查找到 然后进行删除 最重要的是将链表继续串起来 """ def remove(self, data): # 链表从头开始 current = self.__head # 设置一个前面 目前默认为空 pre = None # 只要不是最后一个 while current != None: # 如果找到了节点 if current.data == data: # 找到了节点 判断是否为第一个 if not pre: # 不是第一个,就把现在的头直接指向下一个节点 # 现在节点的next,如果是现在节点就是current而不是current.next了 self.__head = current.next else: # 是第一个,直接让头pre头部指向下一个节点 pre.next = current.next break # 找到了就要立刻退出! else: # 如果没找到节点,pre指向现在的节点 # 继续向下走 pre = current current = current.next # 测试一下上面的代码是否成立 if __name__ == '__main__': singlist = SingleLinkedList() print("是否为空:",singlist.is_empty()) print("长度为:",singlist.length()) print("开始添加数字5") singlist.append(5) print("是否为空:",singlist.is_empty()) print("长度为:",singlist.length()) print("尾部添加数字7,8,10") singlist.append(7) singlist.append(8) singlist.append(10) print("开始遍历") singlist.travel() print("头部添加数字800") singlist.add(800) singlist.insert(2,233) print("开始遍历") singlist.travel() print("查找是否有233:",singlist.search(233)) print("移除一个10") singlist.remove(10) print("开始遍历") singlist.travel()

共有评论(0)